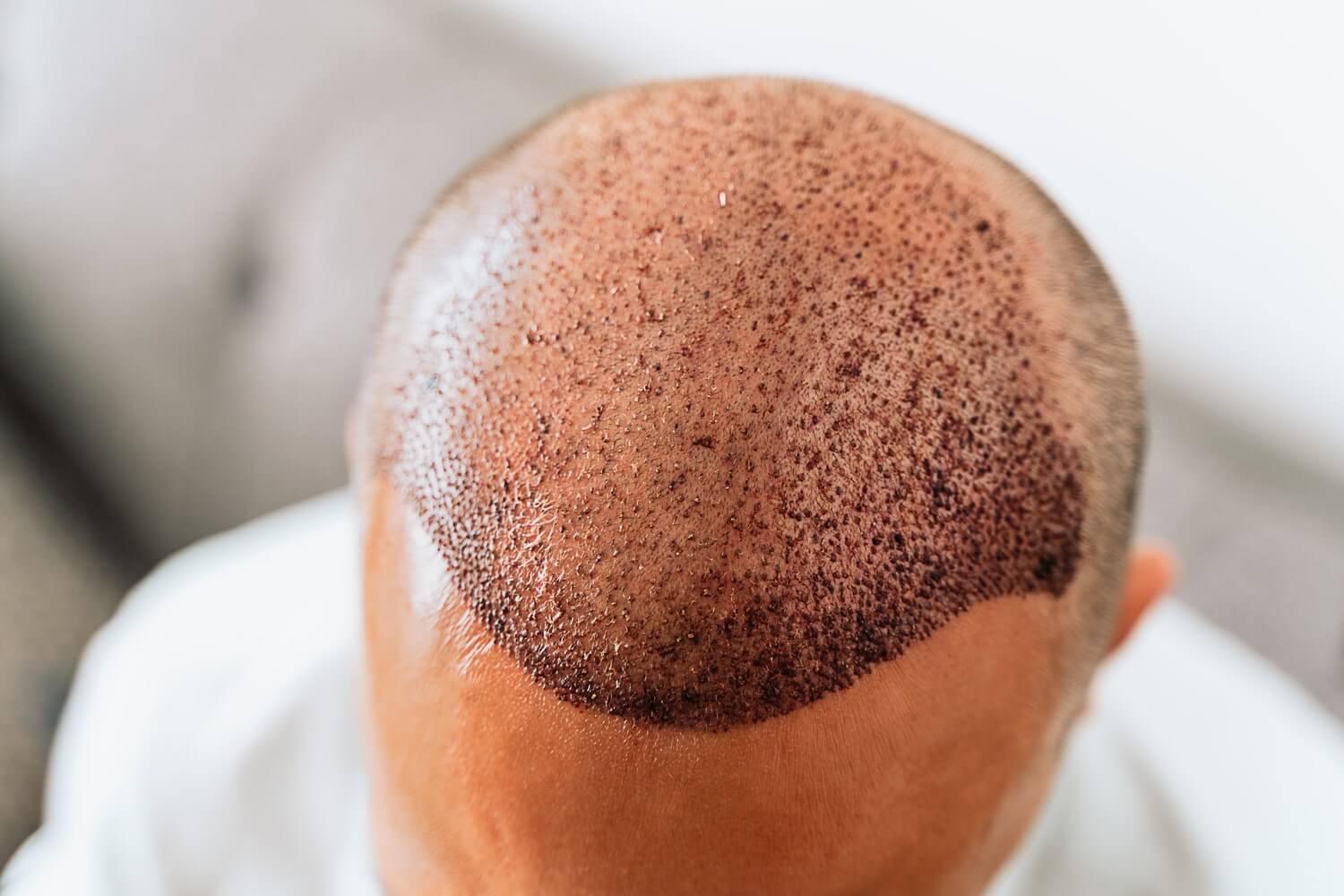
Hair loss is a common concern affecting millions of people worldwide. It can impact self-confidence, appearance, and even emotional well-being. Understanding why hair loss occurs and how modern hair transplants work can help individuals make informed decisions about restoring natural hair growth.
What Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss occurs for various reasons, ranging from genetics to lifestyle factors. Knowing the root cause is crucial for determining the right treatment at
Genetic Factors
The most common cause of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, often referred to as male or female pattern baldness. This hereditary condition makes hair follicles sensitive to hormones, leading to gradual thinning and eventual baldness.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances caused by conditions like thyroid disorders, pregnancy, menopause, or high androgen levels can trigger temporary or permanent hair loss.
Medical Conditions
Certain health issues such as alopecia areata, scalp infections, or autoimmune diseases can damage hair follicles and interrupt natural growth.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Stress, poor diet, smoking, excessive heat styling, and exposure to pollutants can weaken hair, increase shedding, and slow new growth.
How Hair Transplants Restore Hair Growth
Hair transplants are a proven solution for those seeking a permanent, natural-looking restoration.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure where healthy hair follicles are taken from a donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and implanted into areas experiencing hair thinning or baldness.
Techniques of Hair Transplants
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE involves removing individual hair follicles and transplanting them into the bald area. This method leaves minimal scarring, allows faster recovery, and produces natural results.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area. The follicles are then carefully separated and implanted into thinning areas. FUT is particularly useful for covering larger bald regions.
Post-Transplant Hair Growth Process
After a transplant, follicles initially enter a resting phase. New hair growth usually begins within 3–4 months, with visible, full results appearing in 6–12 months. The transplanted hair grows naturally and can be styled like your own hair.
Benefits of Hair Transplants
Hair transplants offer several advantages beyond aesthetic improvement:
-
Natural appearance: Hair grows like your original hair, blending seamlessly.
-
Permanent solution: Transplanted hair is long-lasting and does not require ongoing medication.
-
Low maintenance: Once healed, transplanted hair requires regular care, just like natural hair.
-
Boosts confidence: Restored hair can significantly improve self-esteem and overall appearance.
Who is an Ideal Candidate?
Not everyone is suitable for a hair transplant. Ideal candidates are:
-
Individuals with stable hair loss patterns
-
Those with sufficient healthy donor hair
-
Patients with realistic expectations regarding outcomes
A consultation with a qualified hair restoration specialist is essential to determine suitability and choose the best technique.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hair Post-Transplant
-
Follow all post-operative care instructions from your surgeon
-
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
-
Use gentle hair care products to prevent irritation
-
Attend follow-up appointments to monitor growth
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of hair loss and the science behind hair transplants helps individuals make informed choices about hair restoration. Modern techniques like FUE and FUT provide natural, permanent results, enabling countless people to regain confidence and enjoy a fuller head of hair.