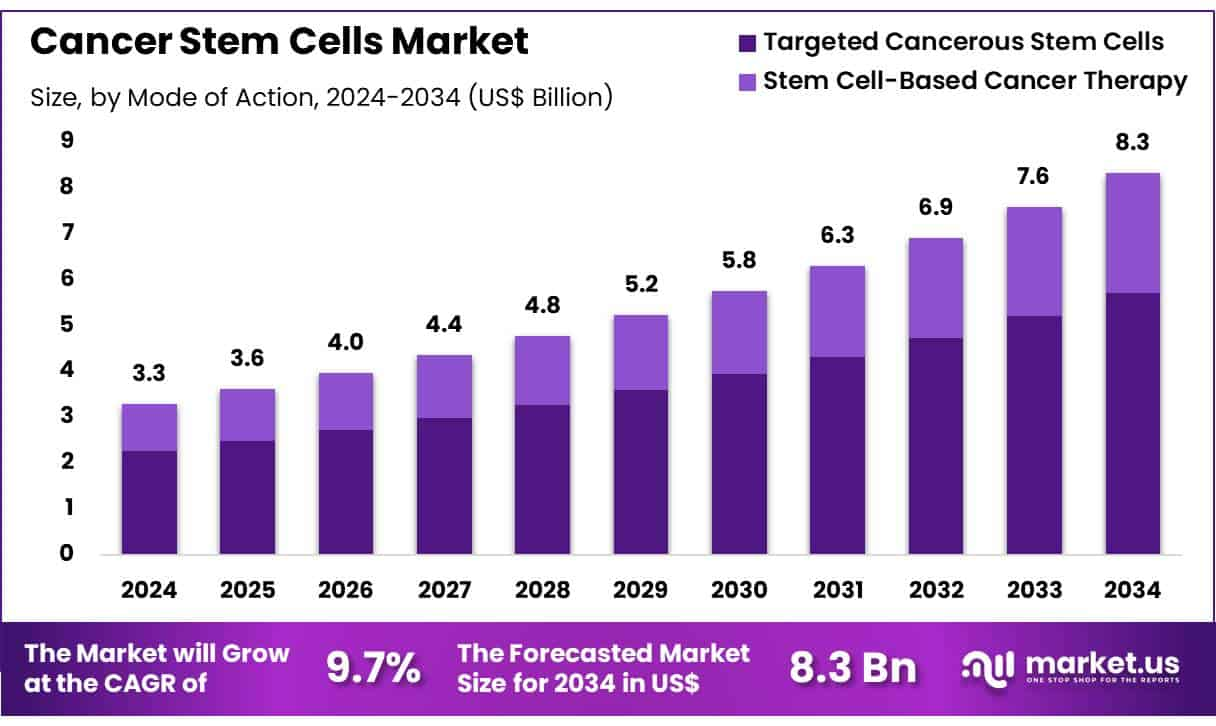
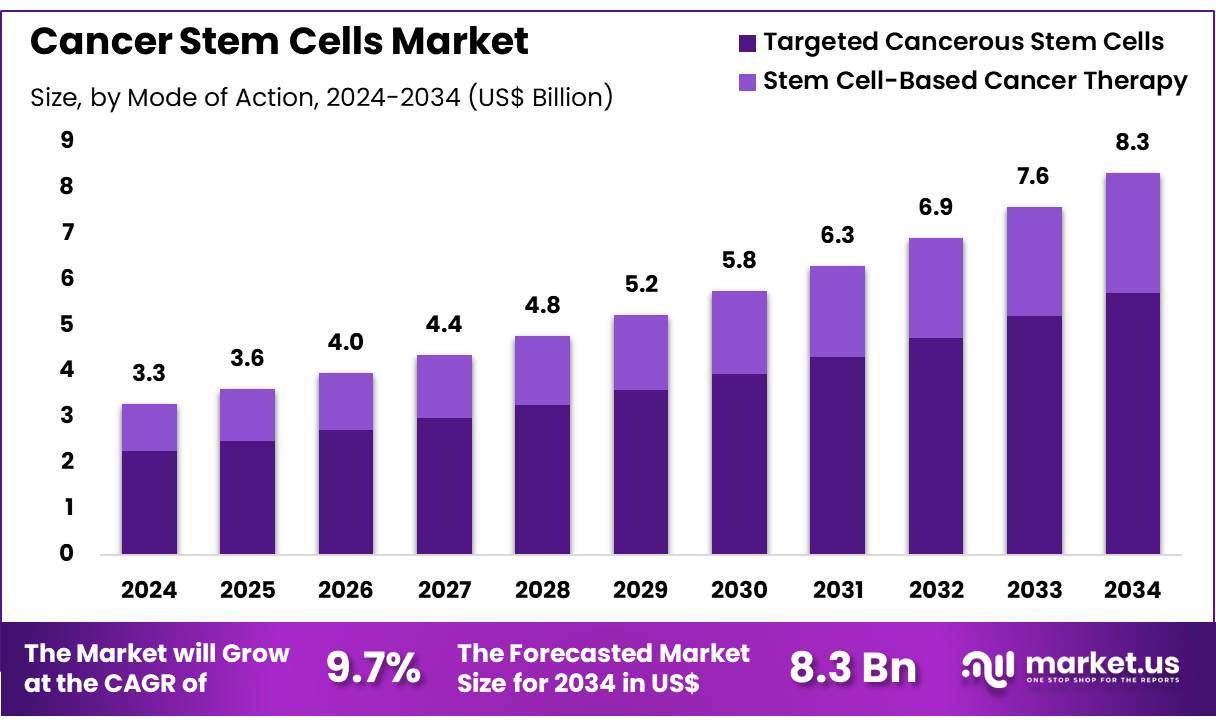
The global Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) market is expected to grow from USD 3.3 billion in 2024 to around USD 8.3 billion by 2034. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.7% during the forecast period. In 2024, North America led the global market with a 38.6% share, contributing over USD 1.3 billion in revenue. The market is expanding due to the rising burden of cancer, increasing investment in research, and advancements in stem cell technologies.
One of the major drivers of market growth is the global rise in cancer cases. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 20 million new cancer cases were reported in 2022. This growing number has increased the demand for more effective and long-lasting treatments. Cancer stem cells are of special interest because they can regenerate tumors and cause relapse after therapy. Their ability to resist standard treatments makes them a key target for future cancer therapies.
Government support is also pushing the CSC market forward. National health agencies across countries like the U.S., Canada, and the UK are funding cancer-related research. For instance, the U.S. National Cancer Institute (NCI) allocates billions of dollars annually for cancer studies, including CSC-related projects. These investments aim to improve early detection, develop better treatment options, and reduce cancer recurrence. Public support for these programs is helping drive both scientific discovery and clinical applications.
Advances in technology are accelerating research and treatment development. Tools like CRISPR gene editing and high-resolution imaging are making it easier to study cancer stem cells in detail. Scientists can now analyze how these cells function and develop therapies to target them directly. This has opened new doors in drug development, including personalized therapies that aim to improve treatment outcomes and reduce resistance. In parallel, the rise of personalized medicine, along with a growing number of global clinical trials focused on CSC therapies, adds strong momentum to the market. With ongoing support from governments and public health organizations, the Cancer Stem Cells market is likely to keep growing in the years ahead.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the cancer stem cells market recorded US$ 3.3 billion in revenue and is projected to hit US$ 8.3 billion by 2034.
- The market is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.7%, signaling steady expansion over the next decade.
- By mode of action, targeted cancerous stem cells dominated in 2023, accounting for 68.5% of the total market share.
- Stem cell-based cancer therapies are also gaining traction but currently trail behind targeted approaches in terms of overall adoption.
- When looking at cancer types, breast cancer treatments held the highest market share in 2023, contributing 52.3% to total revenue.
- Pancreatic cancer and other types formed the remaining share but showed potential for growth through new treatment innovations.
- North America emerged as the leading regional market in 2023, capturing 38.6% of the global market share.
Emerging Trends
1. Focus on Targeted Therapy
More researchers are now creating drugs that attack cancer stem cells (CSCs) directly. These drugs don’t just go after fast-growing cancer cells like traditional treatments. Instead, they focus on the root of the cancer. This method may help lower the chances of cancer returning. It can also reduce the problem of drug resistance. Targeted therapy is a growing area in cancer research. By hitting CSCs directly, doctors hope to stop tumors from growing back. This shift in focus is making treatments more effective and personalized. It offers new hope for long-term cancer control.
2. Combination Treatments Are Gaining Ground
Doctors are now testing therapies that combine CSC-targeting drugs with standard cancer treatments. These include chemotherapy and radiation. The goal is to attack both regular cancer cells and CSCs at the same time. This combined approach may improve treatment success and reduce relapses. It can also stop CSCs from hiding and surviving treatment. More clinical trials are focusing on these dual-action therapies. This trend is important because CSCs often cause cancer to return after treatment. Using a mix of therapies could give patients better and longer-lasting results.
3. Advances in Immunotherapy
Scientists are exploring how the immune system can help fight CSCs. New therapies like CAR-T cell therapy are being tested. These train immune cells to spot and destroy CSCs in the body. Unlike traditional treatments, immunotherapy uses the body's own defense system. This makes it more precise and powerful. Researchers believe this method can reduce side effects and avoid damaging healthy cells. It’s a promising area in cancer research. Many early studies show success in targeting CSCs this way. As more data becomes available, immunotherapy could become a key player in CSC treatment.
4. Increased Use of 3D Cell Culture and Organoids
Scientists are now using 3D cell cultures and organoids to study CSCs. These are tiny lab-grown tumor models. They are more realistic than flat cell cultures. 3D models help researchers see how CSCs behave inside the body. This allows for better testing of new treatments. It also improves drug discovery. These tools are becoming more common in cancer research labs. They make studies more accurate and faster. As a result, researchers can understand CSCs better and find new ways to treat them. This is a big step forward in personalized cancer research.
5. Gene Editing and RNA-Based Approaches
CRISPR and other gene editing tools are being used to target CSCs. These tools can turn off genes that help CSCs survive or spread. This stops the cancer at its root. At the same time, scientists are testing RNA-based methods like siRNA and miRNA. These can block key functions inside CSCs. Both approaches offer precise ways to stop cancer growth. They are still in early stages but show strong potential. Gene and RNA therapies may work well with other treatments too. Together, they could lead to more effective and lasting cancer cures.
Use Cases
1. Preventing Cancer Relapse
Cancer often comes back after treatment. One key reason is the presence of cancer stem cells (CSCs). These cells can survive even when the main tumor is destroyed. CSCs can lie dormant and later start growing again. This makes them a big target for research. Scientists are now developing therapies that aim to destroy CSCs directly. The goal is to stop cancer from coming back after treatment. Targeting these cells may lead to more permanent results. This use case is helping push innovation in cancer drugs. It also gives new hope to patients who have a high risk of relapse.
2. Improving Chemotherapy Outcomes
Chemotherapy is used to kill fast-growing cancer cells. But sometimes, it fails to fully destroy the tumor. That’s because cancer stem cells (CSCs) are often left behind. These cells can survive chemo and rebuild the tumor. To improve this, scientists are testing drugs that target CSCs. These drugs are being used along with chemotherapy. The combination may make cancer treatment more effective. This approach can reduce the chances of cancer returning. It also helps patients respond better to existing therapies. This use case is becoming an important area in clinical trials and drug development.
3. Studying Drug Resistance
Many cancers stop responding to standard treatments. A major reason is drug resistance linked to cancer stem cells (CSCs). These cells have special features that help them survive drugs. Researchers now use CSCs in lab studies to understand how this happens. They grow cancer stem cells and test new drugs on them. This helps identify why certain treatments fail. It also helps design better therapies that can overcome resistance. Studying CSCs in this way is leading to smarter, more targeted cancer treatments. It is also helping doctors choose the right drugs for each patient.
4. Developing Biomarkers for Diagnosis
CSCs have unique proteins on their surface. These markers are not found on normal cells. Scientists are now using these markers to create better diagnostic tools. These tools can detect cancer earlier by identifying CSCs in blood or tissue samples. They can also predict how aggressive the tumor might be. This helps doctors decide the best treatment approach. Biomarkers from CSCs may also be used to monitor treatment progress. If successful, this can lead to faster diagnosis and better outcomes. It’s a growing area in personalized cancer care and early detection.
5. Creating Better Animal Models
To study cancer, scientists use animal models. Traditional models often don’t reflect real human cancer behavior. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are changing that. Researchers now grow tumors in mice using CSCs. These models are more accurate. They mimic how cancer grows and spreads in humans. This helps scientists test new drugs more effectively. It also gives insights into how tumors might behave after treatment. Using CSCs in this way improves the reliability of preclinical studies. It also reduces the risk of failure in later stages of drug development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cancer stem cells market is growing steadily due to rising cancer cases, new technologies, and strong government support. As researchers learn more about how CSCs cause relapse and drug resistance, new treatments are being developed to target them directly. Innovations like gene editing, immunotherapy, and 3D cell cultures are helping scientists create more effective therapies. These advancements also support better diagnostics and personalized care. With more clinical trials and investments in this area, the future of cancer treatment looks promising. The focus on CSCs is not only improving outcomes but also offering long-term hope to patients around the world.