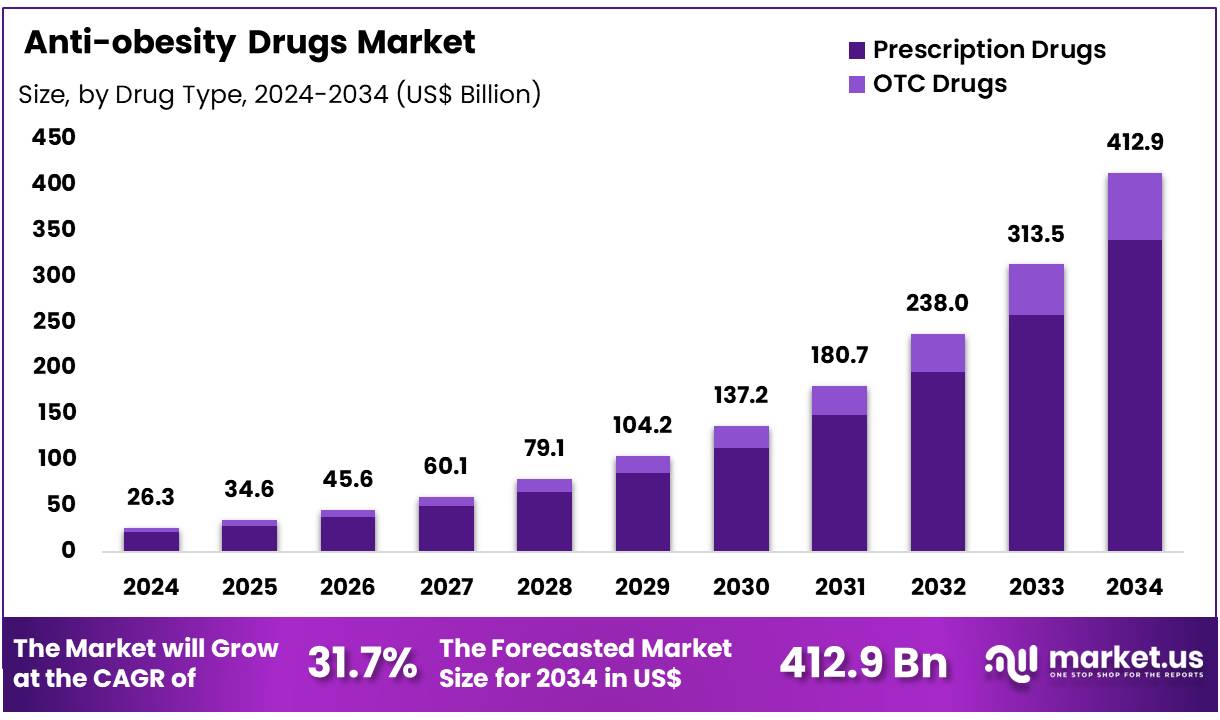
The global anti-obesity drugs market is projected to grow significantly from US$ 26.3 billion in 2024 to an estimated US$ 412.9 billion by 2034. This reflects a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 31.7% during the forecast period. North America currently leads the market, accounting for more than 46.4% of the total revenue, with US$ 12.2 billion in 2024.
One major factor fueling market growth is the increasing burden of obesity-related diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights that obesity significantly raises the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and certain cancers. These chronic conditions are both life-threatening and financially draining for healthcare systems. As a result, governments and healthcare providers are turning to anti-obesity medications to reduce long-term treatment costs and improve health outcomes. Preventive drug use is gaining traction as a practical tool to manage the global obesity crisis.
Support from international and national health authorities is further boosting the market. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have approved several innovative anti-obesity drugs in recent years. These regulatory green lights have encouraged pharmaceutical companies to invest more in R&D. Additionally, some national health guidelines are now recommending drug-based interventions for patients who do not benefit from diet and exercise alone. This regulatory support is opening new opportunities in both developed and developing countries.
Changing lifestyles are also a major contributor to the rising demand for anti-obesity treatments. The growing consumption of calorie-rich, processed foods, along with sedentary habits, is leading to increased obesity rates, especially in urban settings. As people become more aware of the health risks linked to obesity, many are turning to medical help for weight loss. This growing demand for pharmaceutical interventions is pushing the market forward and encouraging the development of more accessible and effective drugs.
Expanding healthcare access in emerging regions is also playing a key role in market expansion. Countries in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are seeing improvements in medical infrastructure and public health awareness. Government-led campaigns targeting obesity prevention and treatment are making a difference by promoting healthy lifestyles and encouraging the use of medications when needed. As these efforts continue, the global anti-obesity drugs market is expected to grow at a rapid pace in the years ahead.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the global anti-obesity drugs market reached US$ 26.3 billion and is projected to hit US$ 412.9 billion by 2034.
- The market is growing rapidly with a strong CAGR of 31.7%, highlighting rising demand for effective weight management solutions worldwide.
- Prescription drugs led the market in 2024, accounting for 82.3% of the total revenue across all anti-obesity drug types.
- Peripherally acting drugs were the top-performing mechanism of action, bringing in 58.5% of the total market revenue in 2024.
- Injectable drugs emerged as the leading route of administration, contributing 75.9% to the global market revenue in 2024.
- Adults made up the primary user group, holding a commanding 95.3% share of the anti-obesity drugs market in 2024.
- Retail pharmacies stood out as the top distribution channel, accounting for 56.7% of all sales in the market during 2024.
- North America dominated regional sales, capturing 46.4% of the global anti-obesity drug market revenue in 2024.
GET SAMPLE REPORT : https://market.us/report/global-anti-obesity-drugs-market/request-sample/
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America captured 46.4% of the anti-obesity drugs market. This dominance is due to high obesity rates, advanced healthcare systems, and high healthcare spending. The United States is the key driver, with a surge in the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide. These drugs are increasingly used for weight loss and related health conditions. Strong pharmaceutical investments and early access to innovations also support North America’s leadership in this growing sector.
According to the latest KFF Health Tracking Poll, about 12% of U.S. adults have used a GLP-1 agonist. These drugs help treat obesity, diabetes, and reduce cardiovascular risks. Among users, 6% are currently on such medication. Usage is much higher among people with specific health conditions. For instance, 43% of adults with diabetes use these drugs. Similarly, 25% of adults with heart disease and 22% diagnosed as overweight or obese also report use. This reflects increasing demand in targeted groups.
Public awareness of GLP-1 drugs is also on the rise. Around 32% of U.S. adults now say they have heard "a lot" about these medications. This is a notable increase from 19% in July 2023. Widespread media coverage and marketing by pharmaceutical firms have played a big role. More people are now seeking medically approved weight-loss options. These factors collectively contribute to a strong market base in North America. Growing interest will likely sustain the region’s lead in coming years.
India is also becoming a key market. The launch of Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy in India signals growing demand. More patients are now open to using prescription drugs for weight loss. Japan’s aging population and lifestyle changes are driving adoption as well. Importantly, the expected launch of generic semaglutide after 2026 will make treatments more affordable. This will likely increase access and boost sales. With these drivers, Asia Pacific is set to record the highest CAGR in the coming years.
