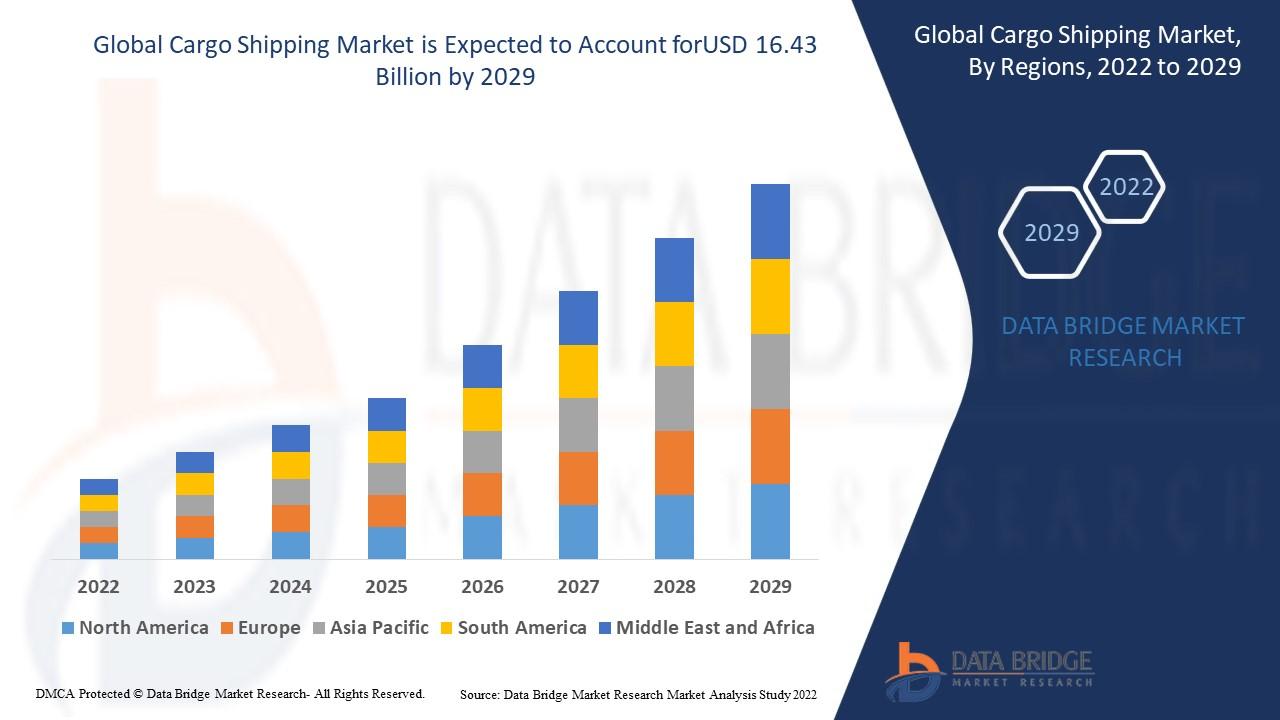
The Cargo Shipping Market stands as the backbone of international trade, facilitating the movement of goods across continents and connecting producers with consumers in every corner of the world. From crude oil and automobiles to consumer goods and machinery, cargo shipping is the essential lifeline of global commerce. In recent years, the market has undergone transformative changes driven by globalization, technological advancements, sustainability efforts, and disruptions such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions. As industries adapt to a dynamic environment, the cargo shipping market continues to evolve, presenting both opportunities and challenges for stakeholders worldwide.
Market Overview
Cargo shipping refers to the transportation of goods and commodities through sea routes using container ships, bulk carriers, tankers, and general cargo vessels. It is the most cost-effective and energy-efficient mode of transporting large volumes of goods over long distances. The industry is integral to global supply chains, with approximately 80% of international trade volume and over 70% of trade value being carried by sea.
The market has been witnessing consistent growth due to the surge in global trade, increasing demand for consumer goods, industrialization in developing regions, and advancements in shipbuilding technologies. According to industry estimates, the cargo shipping market is projected to expand at a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the next decade, supported by the recovery of manufacturing activities, expanding e-commerce, and the growing emphasis on green logistics.
Stay ahead with crucial trends and expert analysis in the latest Cargo Shipping Market report. Download now:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cargo-shipping-market
Key Market Drivers
1. Globalization and International Trade Expansion
One of the most significant factors driving the cargo shipping market is the steady growth of global trade. The integration of economies, free trade agreements, and the rise of global manufacturing hubs such as China, India, Vietnam, and Mexico have contributed to the increasing volume of goods transported by sea. The rise of just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing systems and global supply chain interdependencies have further reinforced the need for efficient maritime transport.
2. Growth of E-commerce and Consumer Demand
The exponential growth of e-commerce has revolutionized global trade logistics. Consumers now demand faster, cheaper, and more reliable deliveries across borders. This trend has led to increased container traffic and demand for intermodal logistics solutions, particularly in developed and emerging economies. Cargo shipping companies are investing heavily in digital tracking systems, automated ports, and optimized shipping routes to cater to the e-commerce boom.
3. Advancements in Maritime Technology
Technological innovations have transformed the cargo shipping landscape. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and big data analytics has enhanced fleet management, route optimization, and predictive maintenance. Smart ports equipped with automated cranes and digital monitoring systems have improved operational efficiency and reduced human errors. Additionally, the development of ultra-large container vessels (ULCVs) has increased cargo capacity and reduced transportation costs per unit.
4. Emphasis on Environmental Sustainability
The shipping industry is under increasing pressure to reduce carbon emissions and adopt sustainable practices. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has introduced strict regulations to limit sulfur emissions and encourage the use of cleaner fuels. As a result, companies are transitioning to liquefied natural gas (LNG)-powered vessels, exploring hydrogen and ammonia fuels, and investing in energy-efficient designs and renewable energy solutions such as wind-assisted propulsion.
Market Segmentation
By Cargo Type
-
Container Cargo: Includes consumer goods, electronics, and machinery transported in standardized containers. This segment dominates global maritime trade.
-
Bulk Cargo: Comprises raw materials like coal, iron ore, and grains. Bulk carriers play a key role in supporting industrial and agricultural supply chains.
-
Liquid Cargo: Involves oil, gas, and chemical transportation through specialized tankers.
-
General Cargo: Consists of items not suited for containerization or bulk handling, including vehicles, project cargo, and heavy equipment.
By Industry
-
Manufacturing and Automotive
-
Oil and Gas
-
Food and Beverages
-
Retail and Consumer Goods
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Mining and Metals
By Region
-
Asia-Pacific: The largest market, led by China, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore. This region serves as the world’s manufacturing and shipping hub.
-
Europe: A mature market with advanced port infrastructure and strong regulatory frameworks.
-
North America: Driven by trade between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, and rising imports from Asia.
-
Middle East & Africa: Growing importance due to oil exports and expanding port development projects.
-
Latin America: Emerging potential fueled by exports of agricultural and mining products.
Market Challenges
1. Supply Chain Disruptions
Events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, port congestion, and geopolitical conflicts (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) have exposed vulnerabilities in global shipping networks. Container shortages and delays have significantly impacted trade efficiency and increased freight costs.
2. Rising Fuel and Operational Costs
Fuel remains one of the largest cost components in maritime transport. Fluctuating oil prices, along with regulatory mandates for cleaner fuels, have increased operating expenses.
3. Environmental Regulations
Compliance with IMO 2020 and other emissions regulations has required massive investments in retrofitting vessels, installing scrubbers, and developing alternative fuel systems.
4. Labor Shortages and Port Congestion
Global shipping faces workforce shortages, particularly among skilled seafarers and port workers. Port congestion, especially in major trade hubs like Los Angeles, Shanghai, and Rotterdam, continues to disrupt schedules and increase turnaround times.
Emerging Trends
1. Digitalization and Smart Shipping
The adoption of digital solutions is transforming fleet operations. Blockchain ensures transparent documentation and reduces fraud, while AI-driven analytics enhance predictive maintenance and route optimization.
2. Automation and Autonomous Ships
Major companies are investing in autonomous vessels to improve safety and efficiency. These ships, equipped with advanced navigation and remote monitoring systems, are expected to reduce human error and lower operational costs.
3. Green Shipping Initiatives
Eco-friendly ship designs, electric propulsion, and renewable energy integration are key trends shaping the industry’s sustainable future. Shipowners are exploring hybrid models and renewable energy-assisted propulsion systems to meet carbon neutrality goals.
4. Strategic Port Developments
Countries are expanding and modernizing ports to accommodate larger vessels and increase trade volumes. Initiatives like China’s Belt and Road and India’s Sagarmala project aim to strengthen maritime connectivity and infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape
The cargo shipping market is moderately consolidated, with several major players dominating global trade. Key companies include A.P. Moller–Maersk, Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), CMA CGM Group, Hapag-Lloyd, and COSCO Shipping. These firms focus on fleet expansion, digital transformation, and sustainability to maintain a competitive edge. Strategic alliances and mergers, such as vessel-sharing agreements, are common to optimize resources and enhance route coverage.
Future Outlook
The future of the cargo shipping market looks promising, driven by increasing globalization, technological innovation, and sustainability initiatives. However, stakeholders must navigate complex challenges such as climate change, cybersecurity risks, and trade protectionism. The integration of digital ecosystems, coupled with investment in green technologies, will be the cornerstone of next-generation maritime logistics.
As global economies rebound and trade flows normalize, the demand for efficient, resilient, and eco-friendly cargo shipping solutions will continue to grow. The next decade will likely witness a more connected, intelligent, and sustainable shipping ecosystem—one that not only supports global trade but also contributes to a greener and more resilient world economy.
Browse More Reports:
Global Water Treatment Chemicals Market
Global Ceramics Market
Global Gemstones Market
Global Smart Fleet Management Market
Global Tote Bags Market
Global Tuna Market
Global Cataracts Market
Global Kimchi Market
Global Party Supplies Market
Global Plant-Based Food Market
Global Processed Fruits Market
Global Wearable Devices Market
Global Commodity Plastics Market
Global Dehydrated Food Market
Global Hepatocellular Carcinoma Drugs Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com