Market Overview
The Global Refractory Material Market continues to play an indispensable role in the functioning of heavy industries, manufacturing environments, and large thermal processing systems. Refractory materials are advanced ceramic substances engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, mechanical load, abrasion, chemical corrosion, and thermal shock.
These extraordinary properties enable them to maintain structural integrity and performance in environments where most materials would rapidly degrade. As industries expand globally and production demands intensify, refractory materials remain the backbone of high-temperature manufacturing processes, powering sectors such as iron and steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, petrochemicals, glass, paper and pulp, and many others.
Refractory materials contribute to mechanical durability, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced operational safety across industries. They provide insulation and protect high-temperature equipment like furnaces, kilns, reactors, boilers, incinerators, and smelters. Without high-performance refractories, the cost and safety risks associated with extreme-temperature operations would be drastically higher. This underscores their importance not only as consumables but also as strategic industrial materials that directly influence productivity, process stability, fuel usage, and equipment longevity.
The growing emphasis on industrial efficiency, infrastructure growth, sustainable production, and automation has led to renewed investment in high-quality refractory solutions. Modern refractories are increasingly designed to offer higher thermal endurance, resistance to slag and corrosive media, improved porosity control, consistent microstructure, and longer service life. This transition reflects the global shift toward optimizing energy consumption and reducing maintenance downtime in temperature-intensive sectors.
The ongoing rise in global steel production, cement manufacturing capacity, copper and aluminum smelting, and petrochemical expansions significantly boosts the demand for refractory products. The construction industry’s growth, infrastructure upgrades, and the expansion of automotive and machinery manufacturing further strengthen market prospects. Additionally, the increasing integration of renewable energy systems such as waste-to-energy plants, biomass plants, and concentrating solar power (CSP) plants opens new avenues for refractory applications due to their reliance on high-temperature equipment.
Market Dynamics
The refractory material market is primarily driven by rising industrialization, expanding steel production, and growing manufacturing capacities across the world. The iron and steel industry remains the largest consumer of refractories, accounting for more than half of total demand. Steelmaking requires constant use of refractory linings in ladles, blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces, tundishes, and continuous casting systems. As global steel demand increases for construction, automotive, machinery, shipbuilding, and infrastructure projects, the need for reliable refractory materials experiences parallel growth.
Cement manufacturing is another major driver. Cement kilns operate at extremely high temperatures, often above 1400°C, requiring specialized refractories capable of resisting clinker dust, abrasion, alkalis, and mechanical stress. As developing regions invest heavily in housing, transportation networks, bridges, and commercial infrastructure, cement production continues to expand, driving demand for high-performance refractory linings.
Non-ferrous metal industries such as aluminum, copper, zinc, nickel, and lead rely on refractories for smelting, refining, and shaping processes. These applications require refractories with exceptional resistance to chemical attack and ability to withstand highly corrosive molten metals. Continuous advancements in electric mobility, consumer electronics, renewable energy systems, and lightweight materials fuel the growth of non-ferrous metal demand, positively influencing the refractory market.
The petrochemical sector adds another layer of opportunity as refineries and chemical plants depend on refractories for catalytic cracking units, reformers, heaters, and reactors. Growing energy consumption, increasing production of polymers and plastics, and refinery modernization projects contribute to rising refractory usage.
Moreover, environmental regulations are reshaping the refractory landscape. Industries are increasingly required to minimize emissions, reduce heat loss, and enhance energy efficiency. This encourages the adoption of advanced refractory designs, low-porosity materials, monolithic refractories, and eco-friendly compositions. The introduction of high-purity raw materials and innovations in manufacturing processes—such as automated mixing, robotic installation, and optimized curing techniques—further enhance performance.
Despite the strong outlook, challenges such as price volatility of raw materials like alumina, bauxite, magnesite, and graphite may impact production costs. Additionally, the availability of skilled labor for installation and maintenance remains a concern. However, with continuous technological progress and increased R&D investments directed toward longer-lasting, high-performance refractories, the market is well-positioned for long-term growth.
Regional Analysis
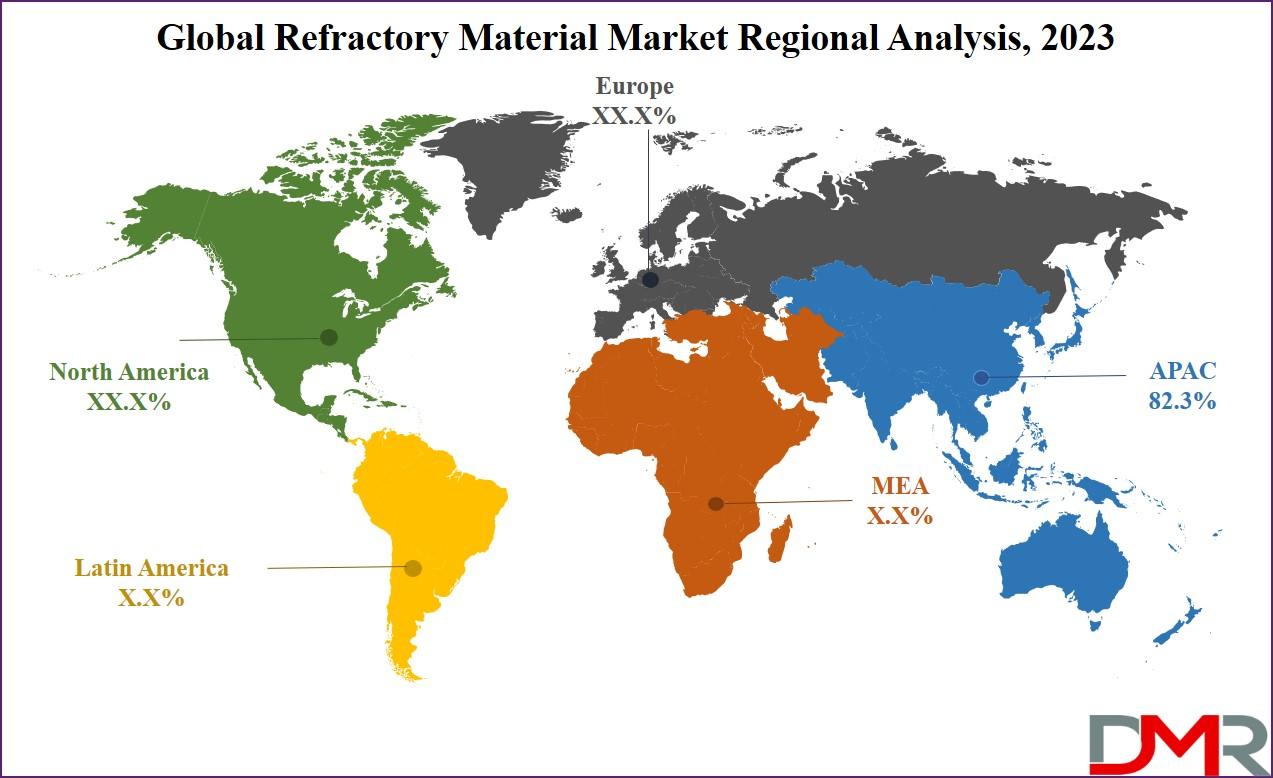
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global refractory material market and accounted for an impressive 82.3% share in 2023. This outstanding market leadership stems from rapid industrialization, large-scale infrastructure development, and massive demand for iron and steel across construction, automotive, manufacturing, and engineering sectors. Asia-Pacific’s strong presence in steel and cement production significantly amplifies its reliance on refractories, reinforcing its position as the industry’s center of gravity.
China remains the world’s largest consumer and producer of refractories due to its enormous steelmaking capacity, extensive cement manufacturing base, and thriving industrial ecosystem. Continuous investments in machinery, construction, transportation networks, renewable energy infrastructure, and heavy industries continue to drive China’s demand for refractory products. The country also benefits from abundant availability of key raw materials, contributing to stable production and competitive pricing.
India is another major growth engine driven by rising urbanization, expansion of automobile manufacturing, construction of smart cities, and major government initiatives aimed at infrastructure transformation. The country’s steel and cement sectors are undergoing rapid modernization, leading to accelerated consumption of high-quality refractory products.
Countries such as Japan and South Korea maintain strong demand due to technologically advanced industrial bases and continuous upgrades in steelmaking, petrochemical refining, and electronics manufacturing. Southeast Asian nations, including Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, are also emerging as important contributors, driven by growing industrial activity and rising investment inflows.
Download a Complimentary PDF Sample Report : https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/refractory-material-market/request-sample/
Market Segmentation
The refractory material market is segmented based on material type, form, application, and end-use industry. These segments highlight the diverse functionality and applications of refractories in high-temperature industrial operations.
In terms of material type, refractories are categorized into clay and non-clay variants. Clay refractories, including fireclay bricks and insulating bricks, are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and reliable performance under moderate temperature ranges. Non-clay refractories—such as alumina, silica, magnesia, zirconia, and carbon-based materials—offer superior properties and cater to industries requiring exceptional thermal and chemical resistance.
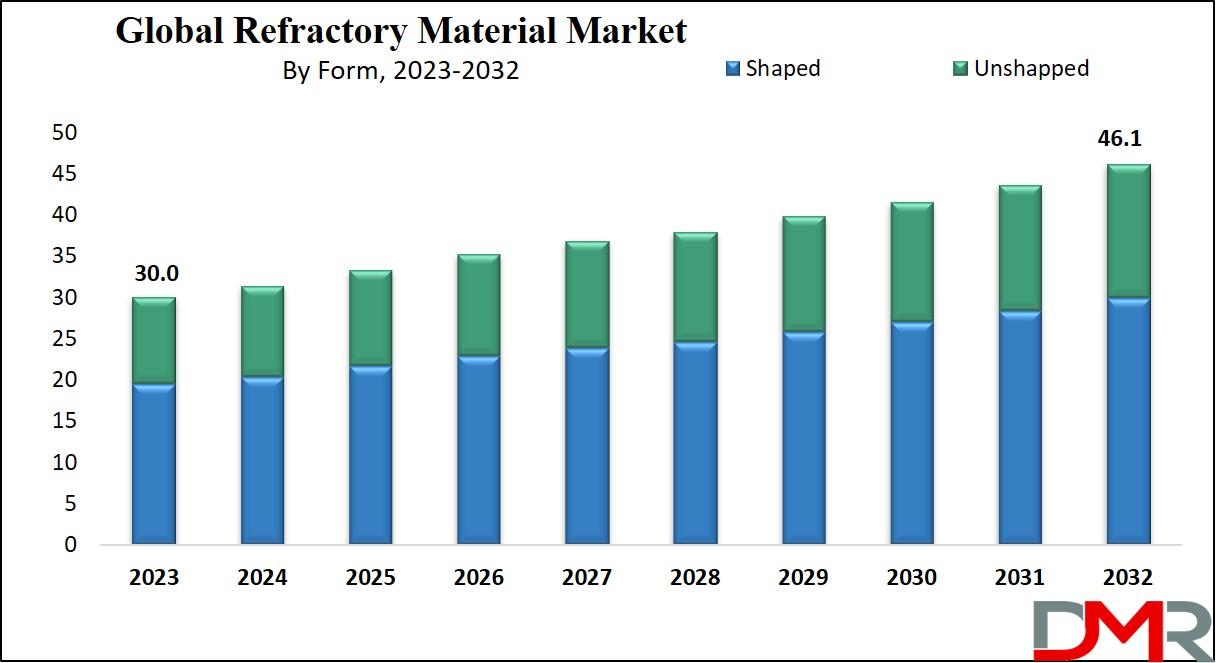
Based on form, refractories are divided into bricks (shaped refractories) and monolithics (unshaped refractories). Brick refractories are traditionally used in fixed installations where precision and stability are essential. Monolithic refractories, which include castables, gunning mixes, ramming masses, and mortars, are gaining popularity due to their easy installation, reduced joints, better structural flexibility, and improved efficiency.
By application, refractory materials are utilized in furnaces, kilns, incinerators, ladles, reactors, and processing units across various industries. Furnaces represent the largest application segment, particularly in the steel, metals, and cement sectors. Kilns account for significant demand as they are essential for cement manufacturing, ceramics production, and mineral processing.
End-use industry segmentation covers iron and steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, petrochemicals, power generation, glass manufacturing, and waste-to-energy systems. Iron and steel remain the primary end-use sector due to the extensive need for refractory linings in every stage of steel production. Cement manufacturing follows closely, requiring diverse refractory solutions for kilns, preheaters, and clinker coolers.
The growing shift toward sustainability also influences material selection. Industries are increasingly adopting refractories that enhance energy efficiency, reduce heat loss, and offer longer operational cycles, which in turn supports the expansion of advanced ceramic technologies.
Competitive Landscape
Competition in the refractory material market is shaped by product innovation, material purity, durability, performance efficiency, and supply chain strength. Manufacturers focus on incorporating advanced compositions, improving thermal shock resistance, and delivering materials capable of withstanding aggressive process environments.
Research and development efforts center around creating refractories with improved strength, corrosion resistance, lower thermal conductivity, and eco-friendly characteristics. Automation in manufacturing processes ensures consistent quality and reduces production variability. Companies are also exploring the use of recycled refractories, aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
Strategic collaborations with steelmakers, cement manufacturers, petrochemical plants, and industrial facility operators play a crucial role in securing long-term demand. Such partnerships strengthen product customization, installation support, and maintenance services. The ability to deliver tailored refractory solutions that suit specific industrial conditions often differentiates leading manufacturers from emerging players.
Additionally, companies are expanding global footprints to serve fast-growing markets in Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Latin America. Advanced installation technologies such as robotic spraying, automated lining equipment, and digital monitoring solutions allow manufacturers to offer enhanced value to end-users, improving operational reliability and minimizing downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are refractory materials and why are they important?
Refractory materials are heat-resistant ceramic substances designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. They are essential for operating furnaces, kilns, reactors, and high-temperature industrial systems safely and efficiently. - Which industries use the most refractory materials?
The iron and steel industry is the largest consumer of refractories, followed by cement, non-ferrous metals, petrochemical refining, and glass manufacturing. Any industry operating high-temperature equipment relies heavily on refractories. - What factors are driving the growth of the refractory material market?
Industrial expansion, rising steel and cement production, infrastructure development, and technological advancements in refractory compositions are key drivers. Growing focus on energy efficiency also contributes to increased demand. - What types of refractory materials are commonly used?
Common types include fireclay, high-alumina refractories, silica, magnesia, zirconia, and carbon-based refractories. Each type is selected based on temperature requirements, chemical environment, and application conditions. - How is technological advancement impacting the refractory market?
Technological advancements have led to high-performance refractories with improved durability, better thermal insulation, lower maintenance requirements, and enhanced corrosion resistance. Automation in installation and monitoring also improves efficiency.
Summary of Key Insights
The refractory material market plays a critical role in global industrial development, supporting high-temperature processes essential for steel, cement, metals, petrochemicals, and several other sectors. With growing industrialization, infrastructure expansion, and rising production demands, the need for durable and efficient refractory solutions continues to rise. Asia-Pacific dominates the market due to massive steel and cement consumption, and its strong industrial ecosystem ensures long-term demand stability. Innovations in material design, sustainability, digital monitoring, and automated installation are reshaping the future landscape of the market. As industries aim for higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption, advanced refractory materials will remain central to high-temperature operations worldwide.
Purchase the report for comprehensive details :
https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/checkout/refractory-material-market/

