The Global Smart Grid Sensors Market is gaining strong momentum as power utilities and governments worldwide accelerate the modernization of electricity infrastructure to support efficiency, resilience, and sustainability goals. Smart grid sensors form the technological backbone of intelligent power networks, enabling real-time data acquisition, monitoring, and control across generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption layers.
As global energy systems evolve toward decentralized generation, renewable integration, and digital control architectures, smart grid sensors are becoming indispensable for maintaining grid stability and optimizing energy flows.
Market Overview
The smart grid sensors market represents a critical segment of the broader smart grid ecosystem, focusing on the deployment of sensing technologies that provide continuous visibility into grid performance and asset health. These sensors measure parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, frequency, power quality, and fault conditions, allowing utilities to detect anomalies, prevent outages, and respond proactively to system disturbances. By transforming traditional grids into data-driven, adaptive networks, smart grid sensors play a central role in improving reliability and reducing operational losses.
The global smart grid sensors market is expected to reach USD 652.8 million by 2025 and expand at a compound annual growth rate of 16.1%, reaching an estimated USD 2,497.7 million by 2034. This rapid growth reflects rising investments in grid automation, the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources, and the urgent need to modernize aging electrical infrastructure. As electricity demand grows and grid complexity increases, utilities are prioritizing sensor-enabled solutions to ensure efficient energy management and system resilience.
Smart grid sensors support the transition from reactive to predictive grid management. Instead of relying on manual inspections and delayed fault detection, utilities can leverage real-time sensor data to identify issues before they escalate. This shift not only improves service reliability but also reduces maintenance costs and enhances customer satisfaction.
Market Dynamics

The dynamics driving the smart grid sensors market are closely linked to structural changes in the global energy landscape. One of the primary growth drivers is the increasing demand for efficient energy management. Urbanization, industrialization, and electrification of transportation are placing unprecedented pressure on power grids. Smart grid sensors enable utilities to balance supply and demand more effectively by providing granular, real-time insights into grid conditions.
Another significant driver is the rapid integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. Renewable generation is inherently variable and decentralized, creating new challenges for grid stability. Smart grid sensors help manage this variability by monitoring power flows, detecting voltage fluctuations, and supporting dynamic grid balancing. Their role is especially critical in distributed energy resource management, where bidirectional power flows must be carefully controlled.
Government policies and regulatory initiatives are also fueling market growth. Many countries are implementing grid modernization programs aimed at improving energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and enhancing grid resilience against extreme weather events and cyber threats. These initiatives often include funding for advanced metering infrastructure, grid automation, and sensor deployment, directly benefiting the smart grid sensors market.
Despite strong growth drivers, the market faces certain challenges. High initial investment costs and the complexity of integrating new sensor technologies with legacy grid infrastructure can slow adoption, particularly in developing regions. Data management and cybersecurity concerns also present barriers, as the proliferation of sensors increases the volume of sensitive operational data. However, ongoing advancements in communication protocols, data analytics, and security frameworks are helping address these challenges.
Technology Landscape and Sensor Types
The smart grid sensors market encompasses a wide range of sensor technologies, each designed to monitor specific grid parameters. Voltage sensors are among the most widely deployed, providing critical data on voltage levels across transmission and distribution networks. Accurate voltage monitoring is essential for maintaining power quality, preventing equipment damage, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Current sensors play an equally important role by measuring current flow through grid components. These sensors support load monitoring, fault detection, and protection system coordination. Temperature sensors are used to monitor transformers, cables, and other critical assets, helping prevent overheating and extending equipment lifespan through predictive maintenance.
Outage detection and fault sensors represent a fast-growing segment within the market. These sensors enable rapid identification and localization of faults, significantly reducing outage duration and restoration times. By pinpointing the exact location of failures, utilities can dispatch repair crews more efficiently and minimize service disruptions.
Advanced sensor technologies are increasingly integrated with communication modules and edge computing capabilities. This allows data to be processed locally, reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making. As communication networks such as 5G and low-power wide-area networks expand, the functionality and scalability of smart grid sensors continue to improve.
Role of Data Analytics and Digital Integration
Smart grid sensors generate vast amounts of data, making analytics and digital integration essential components of the market ecosystem. Advanced data analytics platforms transform raw sensor data into actionable insights, supporting applications such as predictive maintenance, load forecasting, and grid optimization. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in sensor data, enabling utilities to anticipate failures and optimize asset utilization.
Integration with supervisory control and data acquisition systems and energy management systems further enhances the value of smart grid sensors. By providing a comprehensive, real-time view of grid operations, these integrated platforms support informed decision-making and automated control actions. Digital twins, which create virtual representations of physical grid assets, are also gaining traction, relying heavily on sensor data to simulate scenarios and assess system performance.
Application Areas
The application landscape of the smart grid sensors market spans transmission, distribution, and end-user segments. In transmission networks, sensors are used to monitor high-voltage lines, substations, and transformers. These applications focus on ensuring system stability, managing congestion, and preventing large-scale outages.
Distribution networks represent a major growth area for smart grid sensors. As distribution systems become more complex due to distributed generation and electric vehicle charging, sensors provide critical visibility into local grid conditions. This enables utilities to manage voltage levels, detect faults, and optimize network performance at a granular level.
At the consumer and prosumer level, smart grid sensors support advanced metering and demand response programs. By providing real-time consumption data, these sensors empower consumers to manage energy usage more efficiently and participate in grid balancing initiatives. This interactive relationship between utilities and consumers is a defining feature of modern smart grids.
Deployment Models and Infrastructure Considerations
Deployment of smart grid sensors varies depending on grid architecture, regulatory environment, and utility strategy. Urban grids often prioritize high-density sensor deployment to manage complex load patterns and infrastructure constraints. Rural grids, on the other hand, may focus on sensors that enhance visibility across long distribution lines and remote assets.
Infrastructure considerations play a critical role in deployment decisions. Compatibility with existing grid components, communication networks, and data management systems is essential for successful implementation. Utilities are increasingly adopting modular and interoperable sensor solutions that can be integrated incrementally, reducing upfront costs and deployment risks.
Regional Analysis
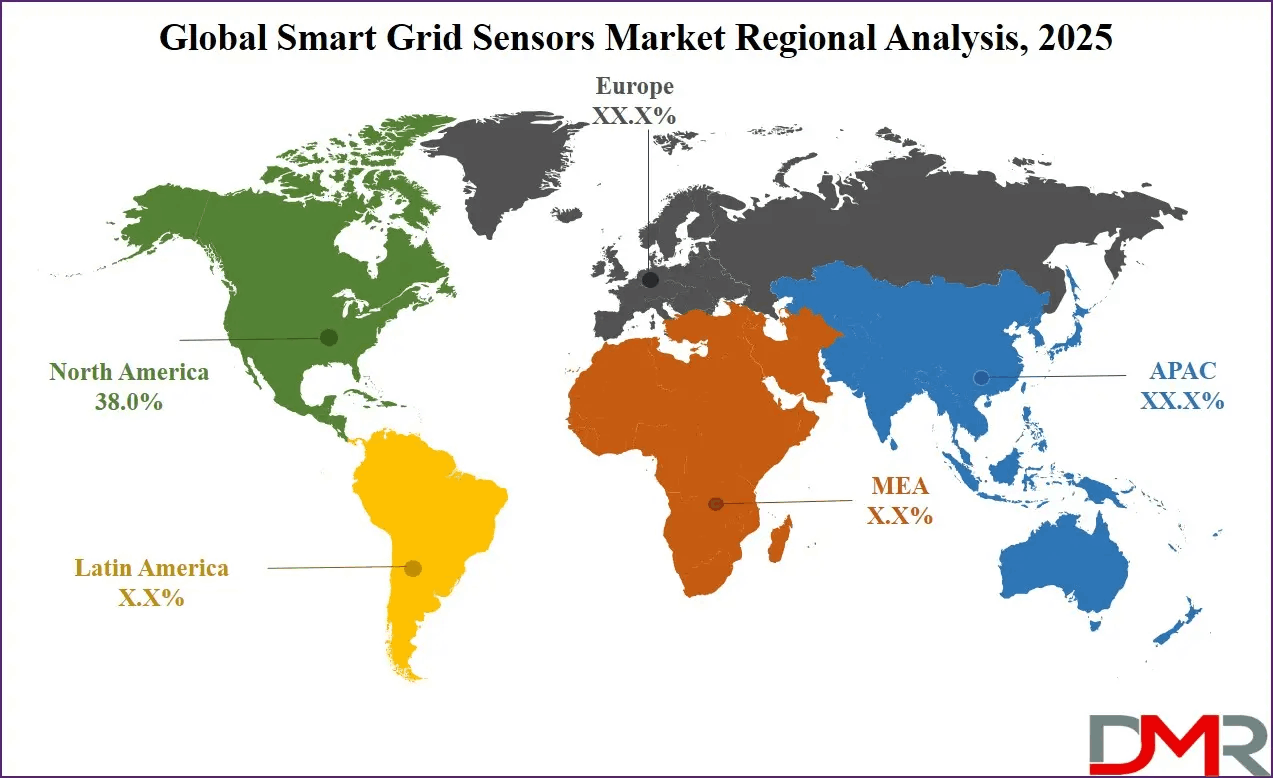
Regional dynamics significantly influence the growth and adoption of smart grid sensors. North America is projected to dominate the smart grid sensors market, accounting for approximately 38.0% of total revenue by the end of 2025. This leadership position is driven by a combination of advanced grid infrastructure, strong regulatory support, and substantial government initiatives aimed at grid modernization.
The United States, in particular, has invested heavily in upgrading aging electrical grids to improve reliability and resilience. Federal and state-level programs focused on smart grid deployment have accelerated the adoption of advanced sensing technologies across transmission and distribution networks. Utilities in the region are leveraging smart grid sensors to enhance outage management, integrate renewable energy, and meet increasingly stringent performance standards.
Europe represents another significant market, characterized by strong emphasis on energy efficiency, renewable integration, and decarbonization. Many countries in the region are deploying smart grid sensors as part of broader energy transition strategies, supporting cross-border power flows and smart city initiatives.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a high-growth market due to rapid urbanization, expanding electricity demand, and large-scale investments in grid infrastructure. Countries in this region are increasingly adopting smart grid technologies to support economic growth, improve power reliability, and integrate renewable energy sources.
Latin America and the Middle East and Africa offer long-term growth potential as governments invest in grid modernization and electrification initiatives. While adoption is at an earlier stage, rising awareness of smart grid benefits is expected to drive future demand for sensor technologies.
Download a Complimentary PDF Sample Report: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/smart-grid-sensors-market/request-sample/
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the smart grid sensors market is shaped by continuous technological innovation and a focus on reliability, accuracy, and interoperability. Market participants are investing in research and development to enhance sensor performance, durability, and communication capabilities. Differentiation increasingly revolves around data accuracy, integration ease, and lifecycle cost efficiency.
Strategic collaborations with utilities, technology providers, and system integrators are common, enabling vendors to align product development with real-world grid requirements. Companies are also expanding their portfolios to offer end-to-end solutions that combine sensing hardware with analytics and software platforms.
Future Outlook
The future of the smart grid sensors market is closely tied to the global energy transition and the rise of digital infrastructure. As grids become more decentralized, dynamic, and data-driven, the demand for advanced sensing solutions will continue to grow. Emerging trends such as artificial intelligence-driven grid management, autonomous grid control, and enhanced cybersecurity will further elevate the role of smart grid sensors.
Long-term growth will also be supported by increasing electrification of transportation and heating, which adds new load patterns and operational complexity to power systems. Smart grid sensors will be essential for managing these changes efficiently and reliably.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are smart grid sensors used for?
Smart grid sensors are used to monitor grid parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, and faults in real time, enabling efficient energy management and improved grid reliability.
Why is the smart grid sensors market growing rapidly?
Growth is driven by grid modernization initiatives, renewable energy integration, rising electricity demand, and the need for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Which sensors are most commonly used in smart grids?
Common sensors include voltage sensors, current sensors, temperature sensors, and outage or fault detection sensors.
Which region leads the smart grid sensors market?
North America leads the market due to advanced infrastructure, strong regulatory support, and significant investments in grid modernization.
How do smart grid sensors support renewable energy integration?
They provide real-time visibility into power flows and voltage conditions, helping manage variability and ensure grid stability when integrating renewable sources.
Summary of Key Insights
The smart grid sensors market is experiencing strong growth as utilities worldwide modernize power infrastructure to meet rising demand, integrate renewable energy, and enhance grid reliability. Advanced sensor technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making across transmission and distribution networks. North America currently leads the market, while Asia-Pacific and other regions present significant growth opportunities. As digitalization and electrification accelerate, smart grid sensors will remain a cornerstone of intelligent, resilient energy systems.
Purchase the report for comprehensive details: https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/checkout/smart-grid-sensors-market/

